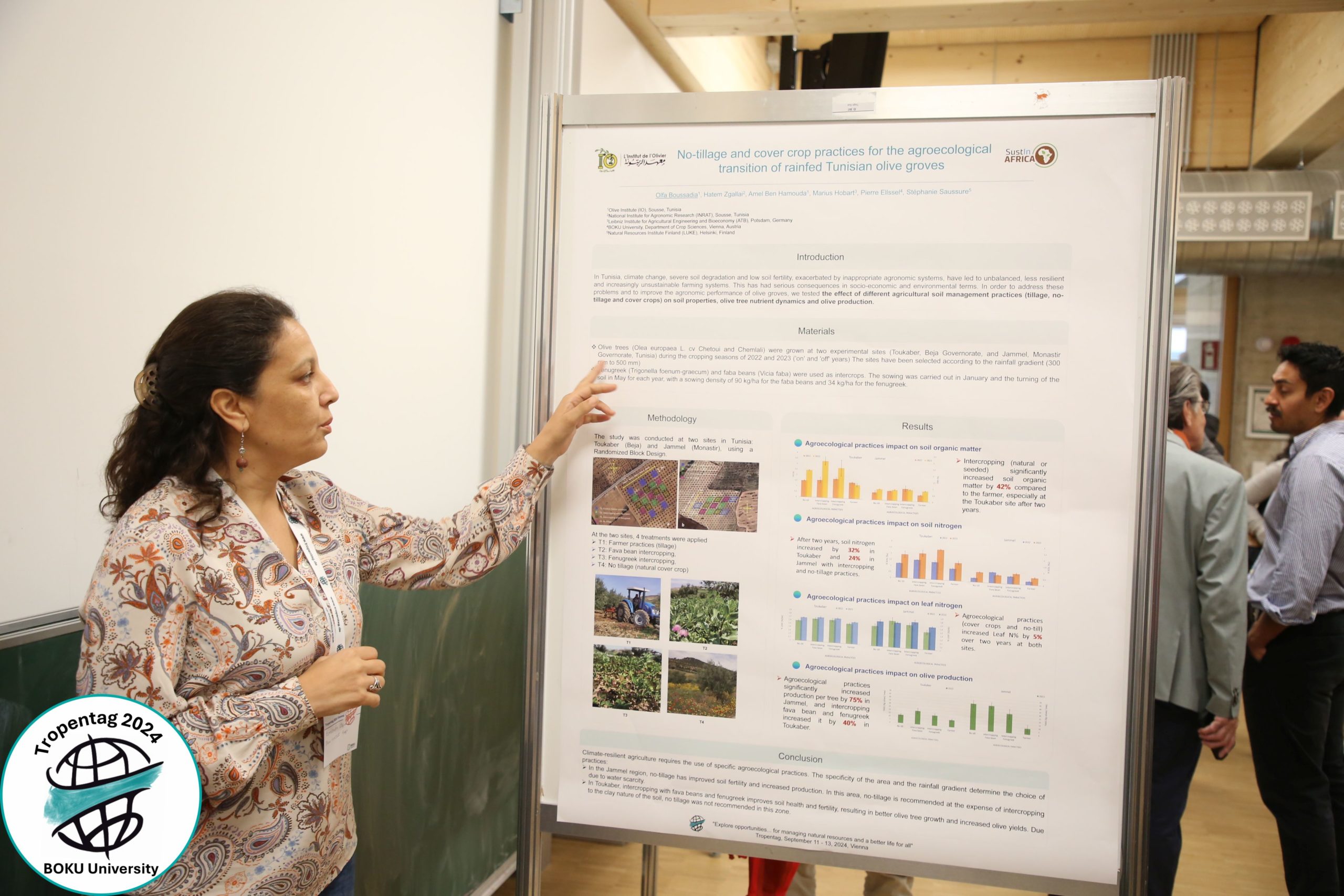
Tunisia, also known as the land of the olive tree, faces environmental crises such as soil degradation, biodiversity loss and climate change. Unsustainable farming practices have exacerbated these issues, pointing to critical need for new practices. Agroecology offers promising pathways for olive growers to create more resilient agricultural systems
For agroecology to be effective, it must be adapted to the local context. An example of a case study at Tropentag 2024 that sheds light on the role of local knowledge in agroecology was presented by Patcharin Sae-Heng (University of Hohenheim): Co-production of Buddhist Agroecological knowledge in Thailand.
Did you know that while there are over 50,000 edible plant species on Earth, just 15 crops provide 90% of the world’s food energy intake? The lack of diversity in our diets not only undermines human health but also reflects the monoculture-dominated landscapes of modern agriculture.
Arts can serve as a powerful medium for deepening the scientific process and communicating complex information to the wider public. Art in science is therefore a central subject at this year’s Tropentag. The conference program includes a variety of activities, bringing an artistic twist to science.